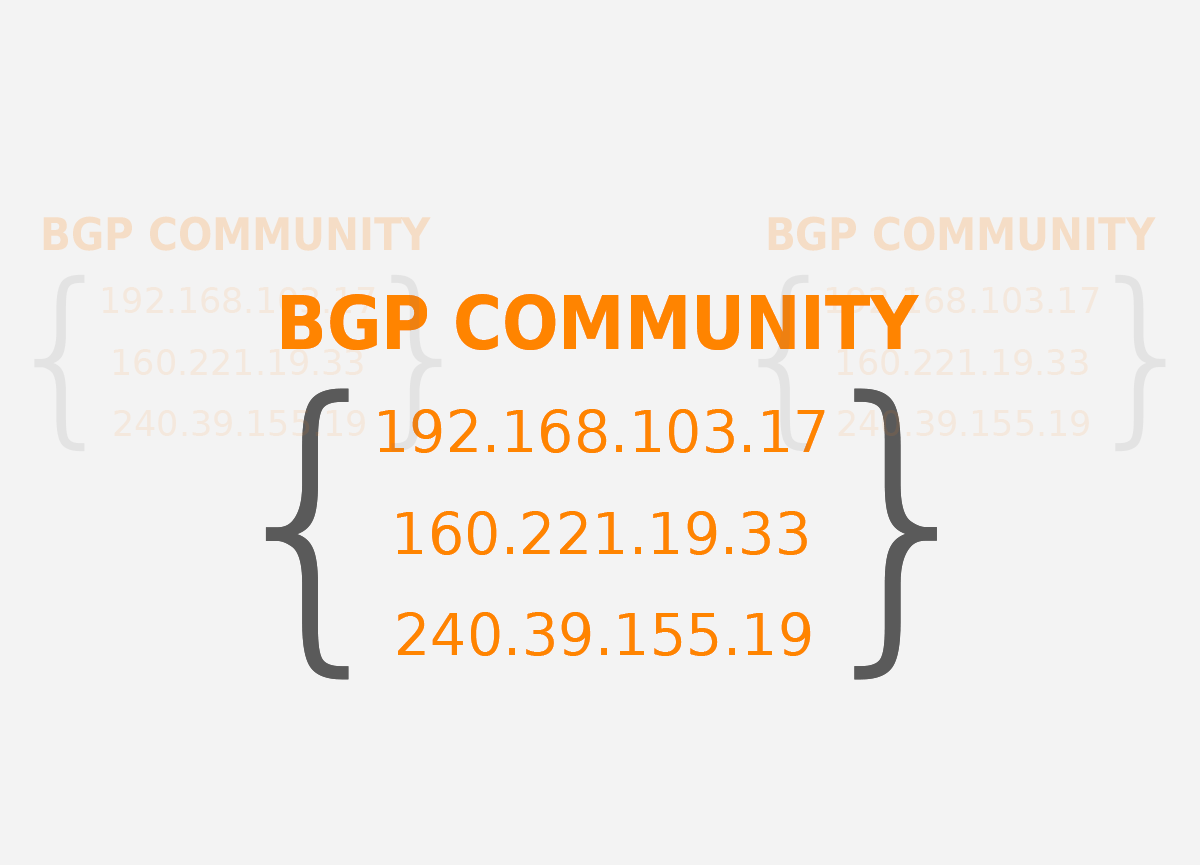Understanding BGP states is essential to grasp how BGP operates. Similar to interior gateway protocols (IGPs) like...
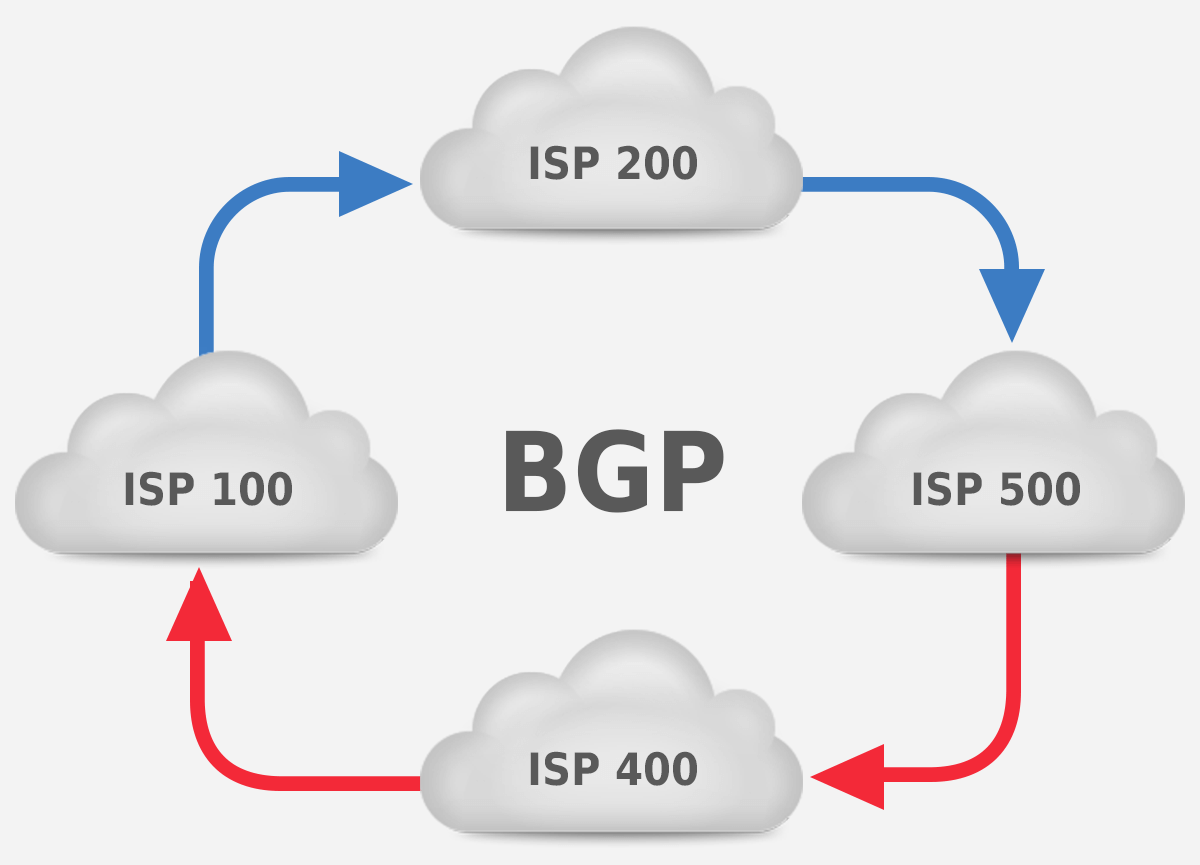
BGP and asymmetric routing
What is asymmetric routing? Asymmetric routing is a network communication scenario where the forward and reverse paths...
Mastering Network Resilience Amidst Africa’s Internet Disruptions: The Advanced Capabilities of Noction IRP
Last week, Africa faced yet again a significant setback in its connectivity infrastructure, with multiple undersea...
BGP flapping, BGP flapping reasons, and the ways to resolve flapping issues
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) serves as the lifeblood of the internet, facilitating the exchange of routing...
Understanding BGP Communities
After reading the title of this article you may be thinking of small neighborhoods in the world's most-connected...
Navigating Undersea Cable Disruptions: Seacom’s Red Sea Connectivity Challenge and Strategic Solutions
Over the recent weekend, the digital world faced a stark reminder of its vulnerabilities when Seacom, a crucial link...
BGP Route Leak prevention and detection via roles in UPDATE and OPEN Messages – RFC 9234
RFC 9234 introduces a novel mechanism that leverages the BGP Role to prevent and detect route leaks. BGP leaks occur...
Geo-blocking at the BGP Level
Geo-blocking at the BGP level is an approach that allows network operators to restrict or control internet traffic by...
Diverting DDoS traffic using the FlowSpec redirect-to-IP next-hop capability (configuration example)
Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks can be a major threat to the availability and security of networks. These...
Diverting DDoS traffic using the FlowSpec redirect via VRF capability. Configuration example.
In the previous article, we described different DDoS attacks and their impact on network infrastructure. We focused on...
BGP traffic rerouting, Flowspec, and the DDoS Scrubbing Centers
When it comes to distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, they are far from a downward trend. Although the...
Optimizing BGP convergence
When there is a change in the reachability of one or more prefixes, BGP needs to do some work to adapt to that change...
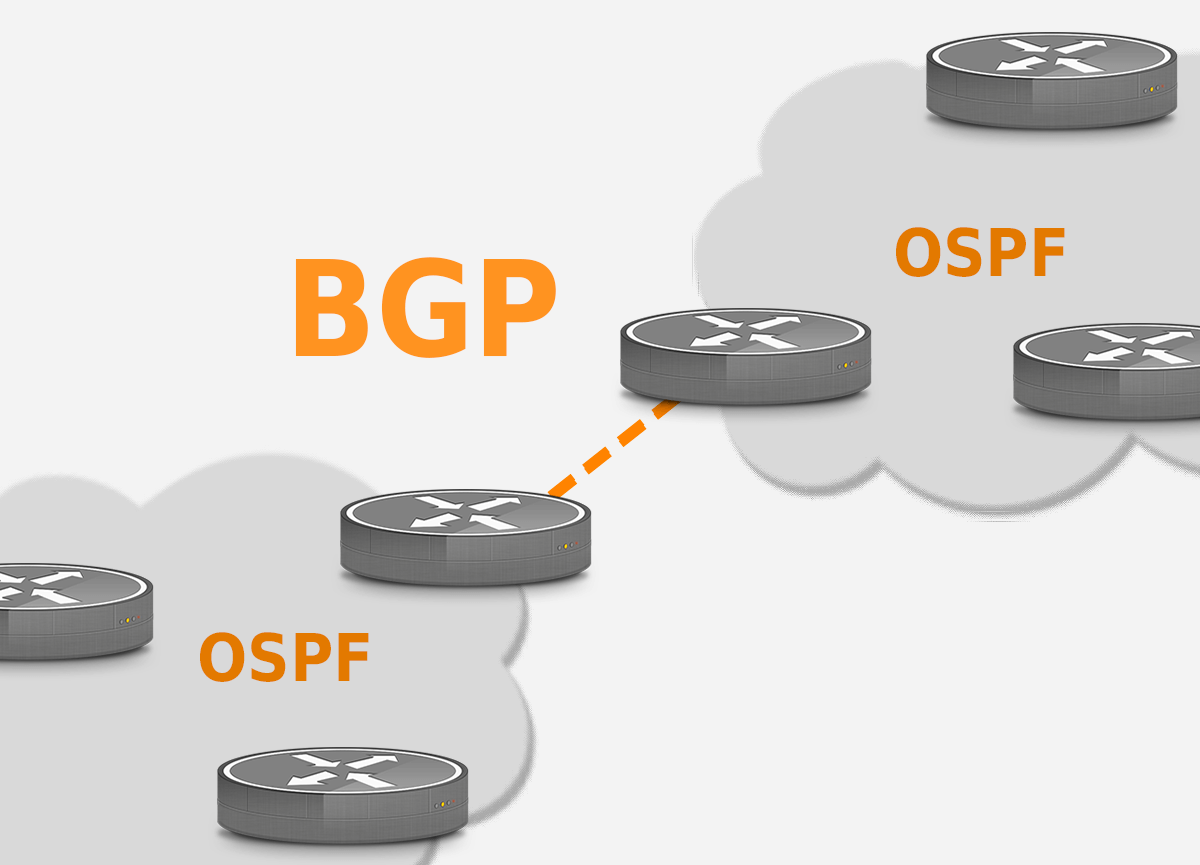
BGP and OSPF. How do they interact?
OSPF and BGP: Differences and Interactions When it comes to routing protocols, two of the most popular are OSPF (Open...
IPv6 Link-Local Next Hop Capability for BGP
When it comes to IPv6, there are several categories of IPv6 addresses, each with its own use case. For example, IPv6...
The Number of the Beast or the Practical usage of the Blackhole Community
BGP blackhole filtering is a routing technique used to drop unwanted traffic. Black holes are placed in the parts of a...
BGP community-based traffic engineering
BGP community attribute is a transitive optional attribute that we use for tagging (marking) a set of prefixes sharing...
IP Transit and the Tiers of Transit Providers
The Internet consists of Internet Service Providers (ISPs) of all shapes and sizes. ISPs have two options when it...
The tightening of Internet control in Russia and potential Internet isolation tech intricacies
The Internet is for everyone, yet not everyone accepts that. In light of the news about Cogent Communications and...
BGP Anycast Best Practices & Configurations
What is Anycast? Anycast is not a new version of IP or the latest networking technology. The RFC 1546 describing...
BGP YANG Model and Configuration
YANG Data Modeling Language Yet Another Next Generation (YANG) RFC 6020 is standard-based data modeling language for...