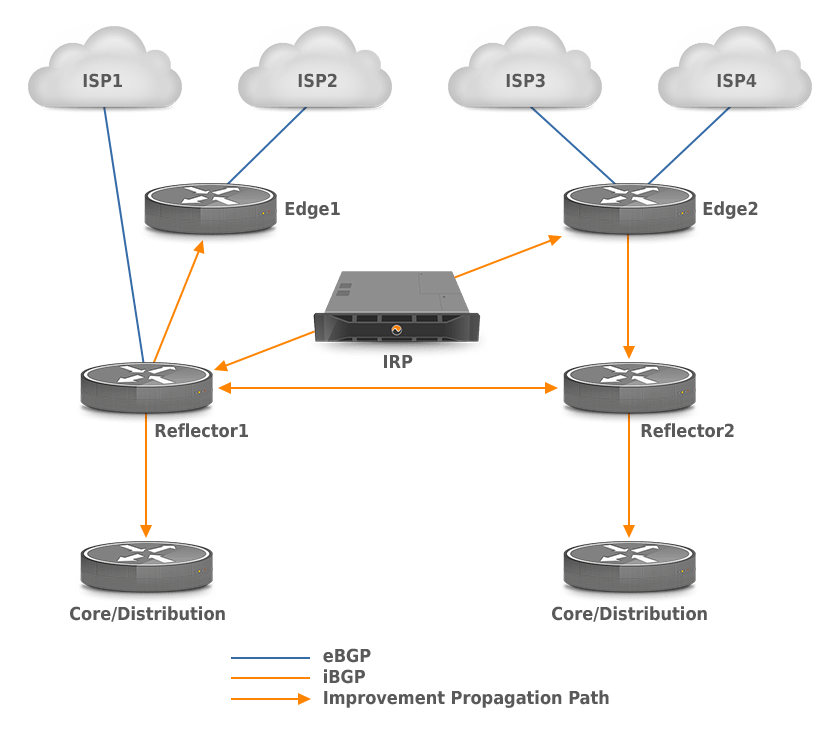
Figure 1.2.4: Support for Centralized Route Reflectors
IRP gives the possibility to advertise routes into one or more route reflectors which subsequently advertise improvements into upper and/or lower routing layers (such as edge, core or distribution).
In case the iBGP sessions can’t be established between the IRP appliance and edge routers, a route reflector is used.
The following restrictions apply for such a solution:
- The Next-Hop-Self option should not be used. A direct iBGP session is required between IRP and each of the divergence points (Reflector1, Edge2) in case it is enabled. This restriction is not applicable between reflectors and core/distribution layers.
- Next-Hop addresses should be accessible (exist in the routing table) where next-hop-self is not applied (Either static routes or IGP is used).
- An Internal Monitor should be configured to retrieve the eBGP session state from the device where the corresponding eBGP session is terminated. For example, ISP1 should be monitored on Reflector1, ISP2 on Edge1, and ISP3 and ISP4 on Edge2.
- Injecting routes to reflector(s) can cause temporary routing loops.