Irpspand acts like a passive network sniffer, analyzing the traffic that is provided to one or more dedicated network interfaces on the IRP server (defined in collector.span.interfaces) from a mirrored port on your router or switch. Irpspand looks up the IP header in the mirrored traffic. When the link level traffic is VLAN tagged as for example in IEEE 802.1Q or 802.1ad for Q-in-Q datagrams, Irpspand will advance its IP packet sniffer past VLAN tags. For better results (higher performance and more analyzed traffic), as specified in the IRP Technical Requirements section, we recommend using Myricom 10Gbps NICs, with Sniffer10G license enabled.
To use the
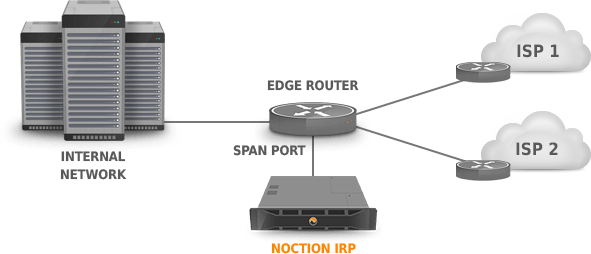
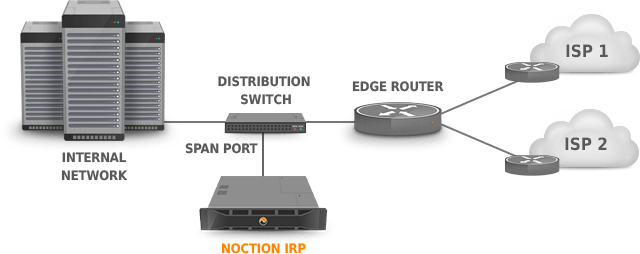
irpspand collector, the following steps must be completed:- Configure port mirroring on your router or switch, as shown in figures (Figure 2.7.2: Span port configuration (on the router)) and (Figure 2.7.3: Span port configuration (on the switch)).or:
- Configure port mirroring on your router or switch, as shown in figures (Figure 2.7.2: Span port configuration (on the router)) and (Figure 2.7.3: Span port configuration (on the switch)).
- Enable the span collector by setting the collector.span.enabled parameter in the configuration file:
collector.span.enabled = 1
- Define the list of network interfaces that receive mirrored traffic, by setting the collector.span.interfaces parameter (multiple interfaces separated by space can be specified):
collector.span.interfaces = eth1 eth2 eth3
- A list of all the networks advertised by the edge routers that IRP will optimize must be added to the configuration. This information should be specified in the collector.ournets parameter.
- In case blackouts, congestions and excessive delays are to be analyzed by the system, the collector.span.min_delay must be turned on as well
collector.span.min_delay = 1