1.3.3.1 Flexible aggressiveness of Commit algorithm based on past overloads #
1.3.3.2 Trigger commit improvements by collector #
1.3.3.3 Commit Control improvements on disable and re-enable #
- when Commit Control is disabled for a provider (peer.X.cc_disable = 1), this Provider’s Commit Control improvements are deleted;
- when Commit Control is disabled globally (core.commit_control = 0), ALL Commit Control improvements are deleted.
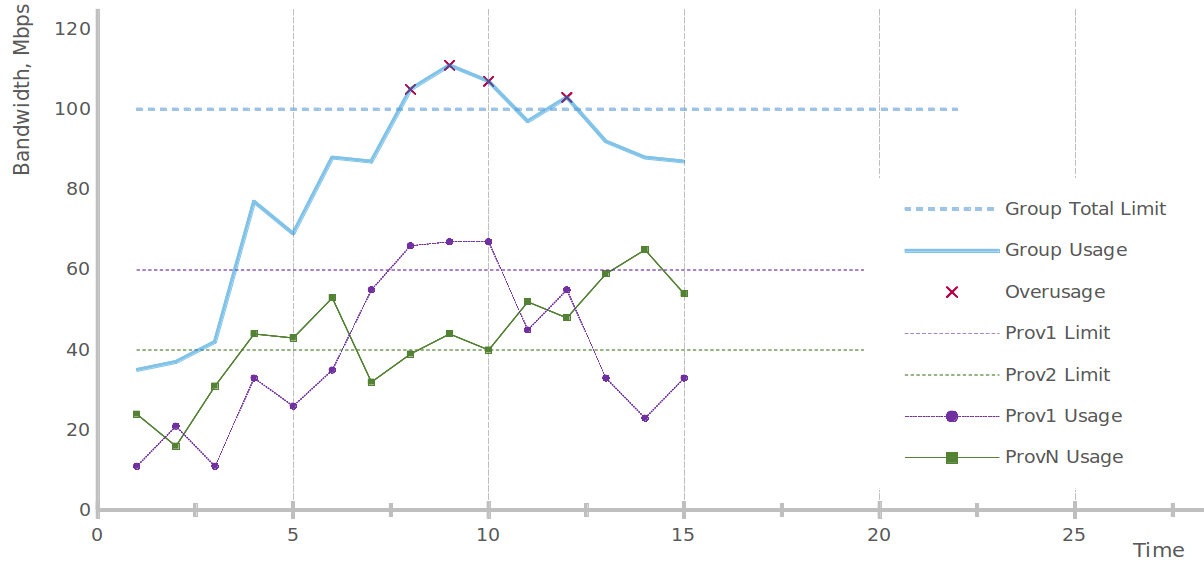
1.3.3.4 Provider load balancing #
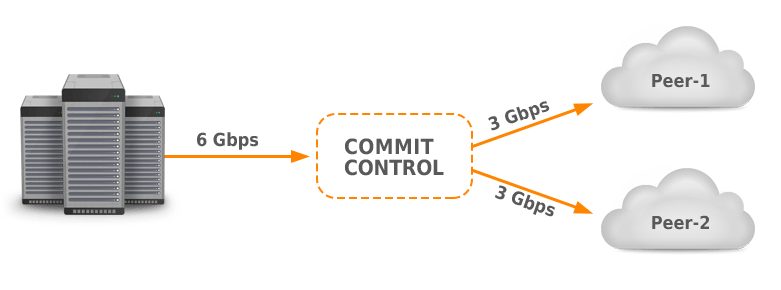
1.3.3.5 Commit control of aggregated groups #
1.3.3.6 95th calculation modes #
IRP supports the following 95th calculation modes:
- Separate 95th for in/out: The 95th value for inbound and outbound traffic are independent and consequently bandwidth control for each is performed independently of each other. For this 95th calculation modes IRP monitors two different 95th for each inbound and outbound traffic levels.
- 95th from greater of in, out: At each time-point the greater of inbound or outbound bandwidth usage value is used to determine 95th.
- Greater of separate in/out 95th: 95th are determined separately for inbound and outbound traffic and the larger value is used to verify if commitments have been met.
1.3.3.7 Interface monitoring #
The feature should be enabled on per-provider basis by setting Interface monitoring type peer.X.mon.interface.type to 1 (Static list) or 2 (Use ifStackStatus).
The feature performs monitoring of interfaces specified in the SNMP Interfaces peer.X.snmp.interfaces parameter. Alternatively, the list can be overridden by the Monitored interfaces peer.X.mon.interface.list parameter.
If the listed interfaces are bonding, but a router does not provide proper speed and interface status for the master interface, then Interface monitoring type peer.X.mon.interface.type can be set to Use ifStackStatus for automatic membership detection, which detects physical interface membership and later uses these physical interfaces to measure the total available bandwidth.
If a router reports inconsistent interface bandwidth then it can be overridden by the Override interface bandwidth peer.X.mon.interface.bandwidth parameter.
bandwidth between Layer2 (for physical interfaces) and Layer3 (for Flow records and internal handling in IRP). The parameter should be decreased if average traffic consists of smaller packets (such as VoIP as ex).