Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is not merely a protocol—it’s the backbone of the...

 BGP community attribute is a transitive optional attribute that we use for tagging (marking) a set of prefixes sharing a common property. Every BGP update carries network information (prefix) along with well-known attributes such as AS Path, Origin information, and Next Hop.
BGP community attribute is a transitive optional attribute that we use for tagging (marking) a set of prefixes sharing a common property. Every BGP update carries network information (prefix) along with well-known attributes such as AS Path, Origin information, and Next Hop.
When we mark the prefix with a particular BGP community, we signal the neighbor router that we want it to perform a specific action for us. In other words, we want it to apply an appropriate routing policy. This includes either a path manipulation (aka traffic engineering) based on the matched community (not the prefix) or BGP route filtering when we do not want or need to advertise the prefix to certain peers, countries, regions, or beyond.
Common path manipulation techniques used by network operators involve changing a local preference (or weight attribute in the case of Cisco gear) based on the received community or AS path prepending. In both cases, a particular path becomes preferred over another for both inbound and outbound traffic. We have devoted an entire article to this topic, along with illustrative examples and configurations for each device, so we encourage you to read it.
It should be added that a downstream router is used to signal desired path manipulation adding BGP community and the upstream router actually performs it based on the matched community. Once the prefix belongs to a particular community, it has access across the network determined by the community policy. Upstream technical support does not need to be involved here to adjust traffic engineering; the control is delegated to the customer.
| NOTE: Multiple communities can be attached to the prefix. The default BGP behavior ensures that communities are stripped from outgoing BGP updates (unless overridden by send-command). |
With well-known (hard-coded) BGP communities it is strictly predefined what the upstream router should do with the prefix to which the community is attached (no-export, no-advertise). For custom communities, we just mark the prefix but it is up to the upstream router to perform an action e.g filter/advertise or set a local preference based on the associated community. The specific actions and the way such communities are implemented is defined by each individual operator and is usually published on the operator’s website. A collection of network operator’s communities is also listed at onestep.net, but its content may not be up-to-date.
Now, let’s have a look at some BGP communities associated with the IPv4 route 23.139.112.0/24 from a different network perspective (Picture 1). The prefix 3.139.112.0/24 is originated from AS53812, NET NV LLC which is an Internet Service Provider located in Reno, Nevada, United States. The prefix is advertised to upstream providers Roller Network – AS11170 and Hurricane Electric LLC – AS6939 (Tier-2). From the AS 6939 perspective, the best path to the prefix 23.139.112.0/24 is learned from the iBGP neighbor 216.218.252.157 with the next-hop 72.52.82.158 (Picture 2). AS_PATH attribute is 53812.
The AS 11170 (Roller Network) has two transit connections – one via AS6939 (Tier-2) and the other one via AS2914 (NTT Global IP Network, Tier-1 network). The Roller Network supports BGP communities for their customers. Let’s say that the customer – AS53812 will lower the customer’s default local preference from 200 to 90 on a connection to AS11170 in order to engineer traffic on the upstream provider’s network. In this case, the AS53812 will tag 23.139.112.0/24 with the community 11170:90. Setting the localpref below 100 will cause the externally learned prefix to be selected. As a result, incoming traffic from other AS11170 customers destined for 23.139.112.0/24 will follow the longer AS path through AS6939 to AS53812. The higher default local preference 100, set for the prefix 23.139.112.0/24 which is received from AS6939 is a real tie-breaker here.
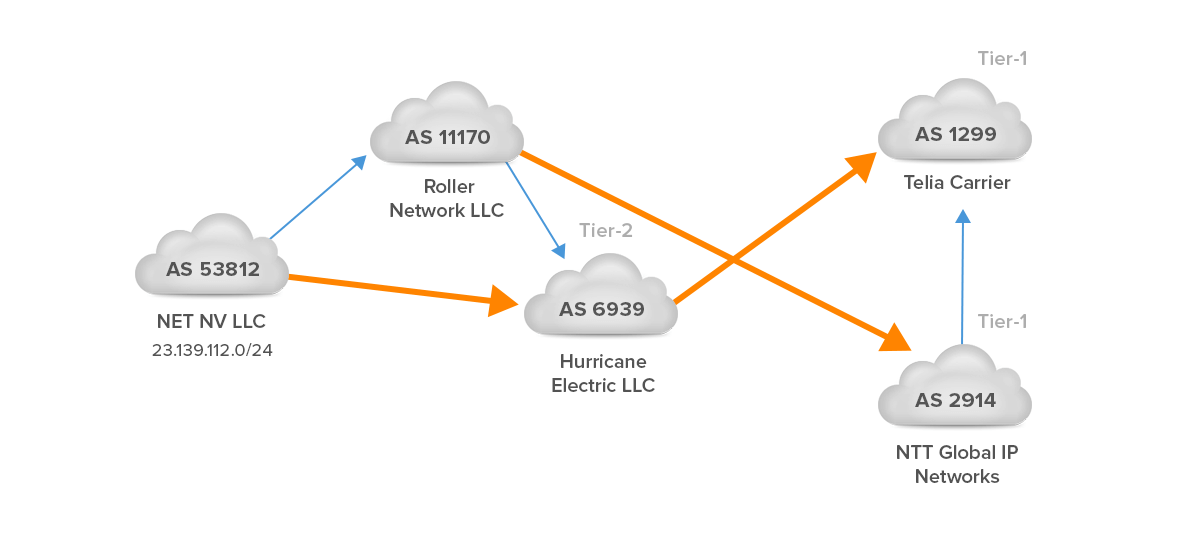
Figure 1 – IPv4 Route 23.139.112.0/24 Originated on AS 53812 and Propagated to AS1299 and AS2914
The BGP communities that the AS11170 supports are published on their website. The AS11170 has dedicated specific BGP communities to suppress announcements to all peers or a particular transit provider. Similarly, they have communities to set AS prepending to transit or peers. For instance, if the customer – AS53812 wants to prepend transit 3x, the AS11170 marks the prefix 23.139.112.0/24 with the community 11170:403. In this case, 11170 is the AS prepended and the AS6939 sees the AS path as 1170 1170 1170 53812.
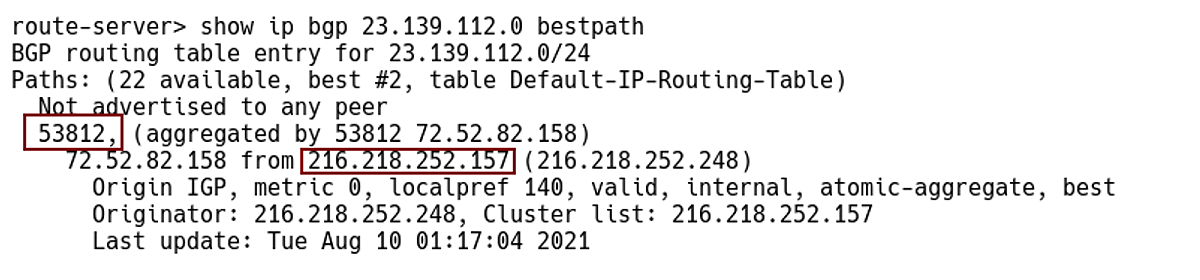
Figure 2 – Checking Best Path for Prefix 23.139.112.0/24 on Route-server 64.62.142.154, Locas AS6939 (Hurricane Electric LLC)
Picture 3 depicts the BGP routing table entry for 23.139.112.0/24 (AS538122, NET NV LLC) from the view of AS2914 (NTT Global IP Network). There is only one route in the table and it has the AS_PATH attribute set to 11170, 53812, 53812, 53812, 53812, 53812, 53812. AS path is prepended several times with ASN 53812 in order to make this route less preferable; we assume that prepending is done by AS53812 itself.
The information communities attached to 23.139.112.0/24 by AS2914 tell more about where the route was learned. According to, NTT customer BGP communities definition, the route was learned as following:
North America MSA origins:
2914:1005 Los Angeles, CA
North American country origins:
2914:2000 us (United States)
World regional origins :
2914:3000 North America
65503:1299 prepend AS 3x to peer 1299
65503:3257 prepend AS 3x to peer 3257
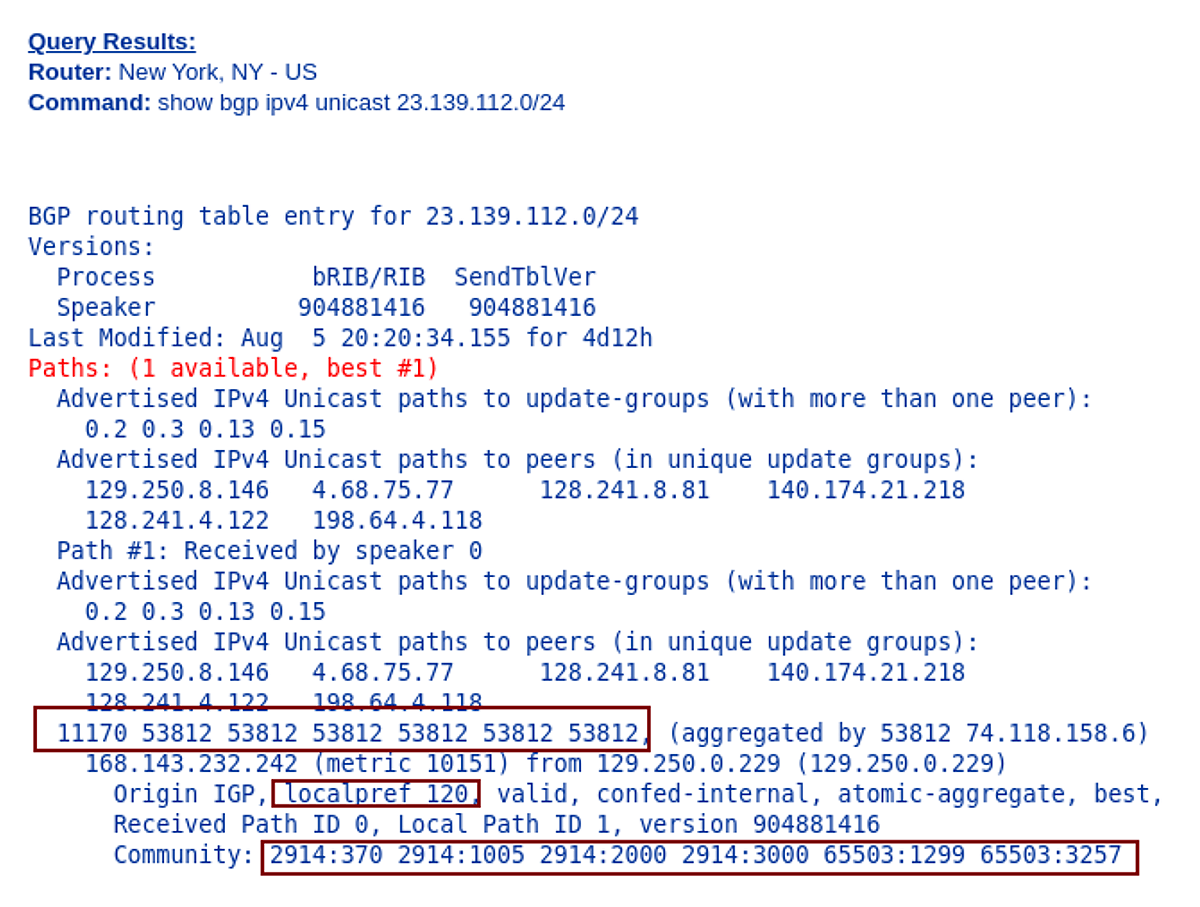
Figure 3 – NTT Global IP Network (AS2914) Looking Glass Look at Prefix 23.139.112.0/24
Picture 4 depicts the BGP routing table entry for 23.139.112.0/24 (AS53812, NET NV LLC) from the view of AS1299 (Telia Carrier). This route is learned from AS2914 and although it is not the best route and thus not installed in the routing table, it will help us analyze the BGP community. The AS2914 has prepended its ASN as instructed by the action community 65503:1299 (prepend AS 3x to peer 1299) which is attached to prefix 23.139.112.0/24 learned from the AS11170.
The prefix 23.139.112.0/24 is also marked with BGP informative communities. More specifically, those are the communities added by AS2914 – 2914:1005 (Los Angeles, CA), 2914:200 (US), and 2914:3000 (North America). Communities 1299:4000, 1299:25), 1299:25600 provide information on how and where the route 23.139.112.0/24 was learned from the view of AS1299. The communities are explained on the Telia Carrier website.
1299: xyzzz
x is BGP Neighbour type; 2 for Peers or 3 for Customers
y is Region; 0 for Europe, 5 for North America or 7 for Asia
zzz is City
So the community 1299:25600 means:
2 – BGP peer
5 – North America
600 – Ashburn / Reston / Manassas
Similarly, the community 1299:25000 denotes a route learned from the North American peer – AS2914.
| NOTE: The localpref 150 is set for peerings. |
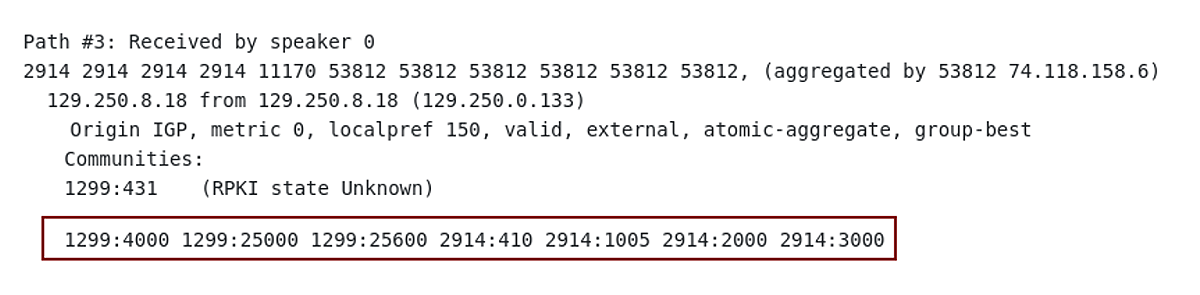
Figure 4 – Telia Carrier (AS1299) Looking Glass Non-Best Path to 23.139.112.0/24
Figure 5 again shows the BGP routing table entry for 23.139.112.0/24 from the A1299 (Telia Carrier) view. This time, however, the figure shows the best route through AS6939 to AS53812. The localpref is 200, which is the default value that AS1299 uses for its customers. The route has attached active communities that deny prefix announcing to specific regions and ASNs. The communities 1299:35000 and 1299:35200 reflect that the route is learned from North American Customers in Palo Alto.
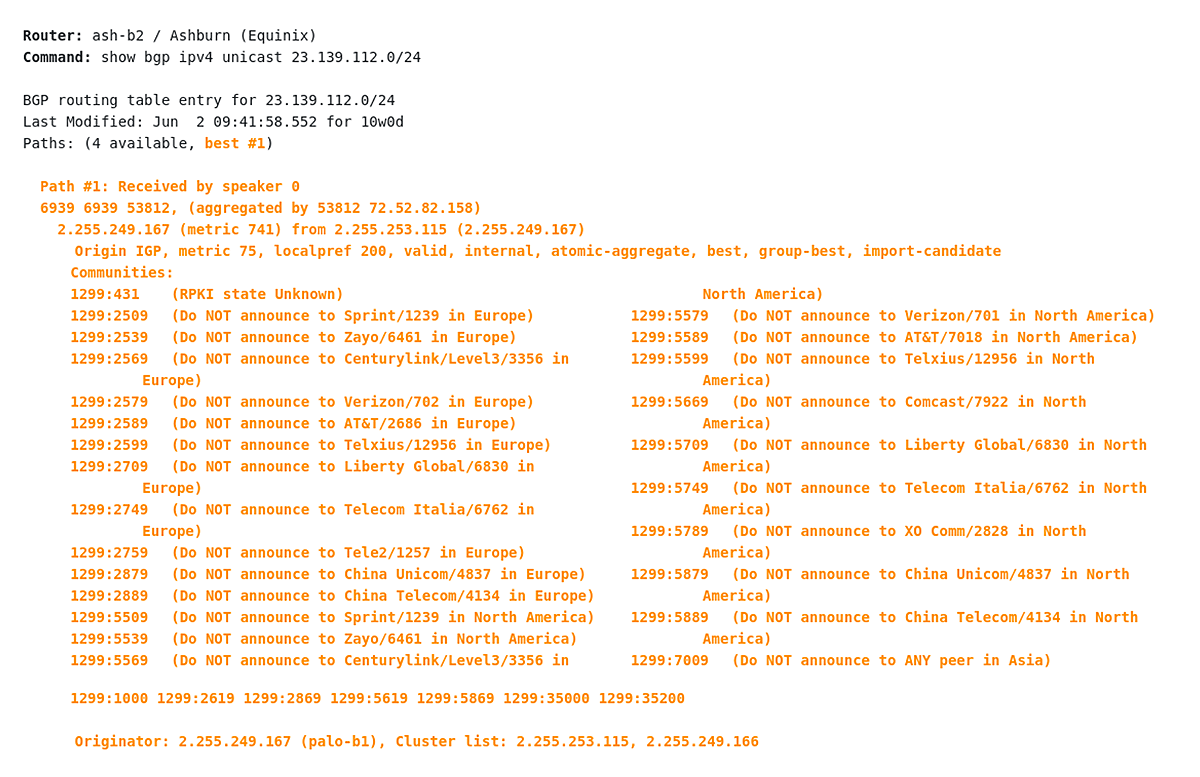
Figure 5 – Telia Carrier (AS1299) Looking Glass Non-Best Path to 23.139.112.0/24
BGP communities are powerful tools that provide customers with the ability to tag announcements to dynamically change certain BGP parameters within service provider networks. However, the upstream service providers are not responsible for routing errors or loss of connectivity due to the use of BGP communities by their customers. Customers should therefore always follow the old adage “With great power must come great responsibility” and closely plan and monitor the use of their own BGP communities.
IRP supports the automated inbound BGP performance optimization starting with version 4.0. This is possible thanks to the automated network performance issue identification by the platform and the use of traffic engineering capabilities to influence inbound traffic routing for the end customers.
Automate BGP Routing optimization with Noction IRP
In recent years, the concepts of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have moved from the academic...
Recent disruptions to two undersea internet cables in the Baltic Sea have yet again highlighted a pressing issue for...
Understanding BGP states is essential to grasp how BGP operates. Similar to interior gateway protocols (IGPs) like...