 The BGP Attribute Filter feature enables BGP speakers to take a certain action based on the presence of a specified path attribute inside the UPDATE message received from a neighbor. Basically, there are two actions which a BGP speaker can take. When the update is treat-as-withdraw and a specific attribute type is matched, the prefix with this attribute inside the UPDATE message is removed from the BGP routing table. However, if the requirement is to drop a specific attribute from the update and the BGP speaker should process the rest of the update normally, the action discard must be configured for the attribute.
The BGP Attribute Filter feature enables BGP speakers to take a certain action based on the presence of a specified path attribute inside the UPDATE message received from a neighbor. Basically, there are two actions which a BGP speaker can take. When the update is treat-as-withdraw and a specific attribute type is matched, the prefix with this attribute inside the UPDATE message is removed from the BGP routing table. However, if the requirement is to drop a specific attribute from the update and the BGP speaker should process the rest of the update normally, the action discard must be configured for the attribute.
The BGP Enhanced Attribute Error Handling feature prevents both iBGP and eBGP peer sessions from flapping when a BGP speaker receives the UPDATE message with the malformed attribute. The malformed Update is treat-as-withdraw and does not cause the BGP session to be reset. This feature is enabled by default, however it can be disabled with the help of a no bgp enhanced-error command. Thanks to BGP Enhanced Attribute Error Handling, valid routes exchanged over a session are not impacted because a BGP speaker does not reset a session when malformed BGP Update is received. RFC 7606 defines the error handling procedures for a number of existing attributes.
As for the matching attributes in an UPDATE message, there are several limitations in the configuration of attribute filtering. For instance, attributes 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 14, 15, and 16 cannot be configured for both path treat-as-withdraw and discard attributes. Attribute type 5 (localpref), type 9 (Originator,) and type 10 (Cluster-id) can be configured for both treat-as-withdraw and discarattributes for eBGP neighbors only.
Let’s explain the differences between the actions treat-as-withdraw and discard for BGP Attribute Filtering using the network topology in Picture 1. The routers IOS-XR (AS 64500) and FRR (AS 64501) are configured to established eBGP session. The FRR router is running Core Linux 9.0 with the installed FRRouting IP routing protocol suite 5.0.2.
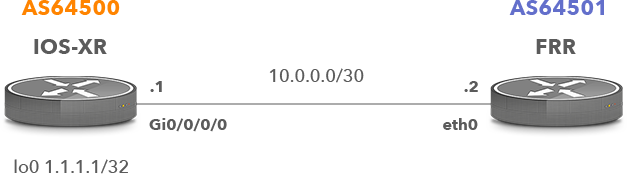
Picture 1: Network Topology
The FRR router advertises prefixes 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24 towards IOS-XR. The community 64500:100 is attached only to the prefix 192.168.1.0/24.
1. Routers FRR and IOS-XR Initial Configuration
1.1 FRR Configuration
interface eth0 ip address 10.0.0.2/30
The route-map Peer-XR is applied to an outbound route 192.168.1.0/24 for a neighbor 1.1.1.1 (IOS-XR).
router bgp 64501 bgp router-id 10.0.0.2 neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 64500 neighbor 1.1.1.1 ebgp-multihop 2 address-family ipv4 unicast network 192.168.1.0/24 network 192.168.2.0/24 neighbor 1.1.1.1 route-map Peer-XR out
A static route to the loopback IP 1.1.1.1 (IOS-XR) is needed to peer with the router IOS-XR.
ip route 1.1.1.1/32 10.0.0.1
Static null routes are configured and presented in a routing table of FRR in order to advertise both routes toward the IOS-XR.
ip route 192.168.1.0/24 blackhole ip route 192.168.2.0/24 blackhole
The sequence 10 of the route-map Peers-XR matches network 192.168.1.0/24 and sets the community 64500:100 for this network. The sequence 20 is needed to permit advertisement of the network 192.168.2.0/24.
access-list 10 permit 192.168.1.0/24 route-map Peer-XR permit 10 match ip address 10 set community 64500:100 route-map Peer-XR permit 20
1.2 IOS-XR Configuration
The IOS-XR router is running Cisco IOS XR Software, Version 6.1.3.
interface Loopback0 ipv4 address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 ipv4 address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252
eBGP peers must have a Route-Policy (route-map) configured to permit routes in and out of them.
route-policy PASS pass router bgp 64500 bgp router-id 1.1.1.1 address-family ipv4 unicast neighbor 10.0.0.2 remote-as 64501 update-source Loopback0 address-family ipv4 unicast route-policy PASS in route-policy PASS out
The prefix 192.168.1.0 is received from the neighbor 10.0.0.2 (FRR) with the attached community 64500:100 (Picture 2).
RP/0/0/CPU0:ios# show bgp 192.168.1.0
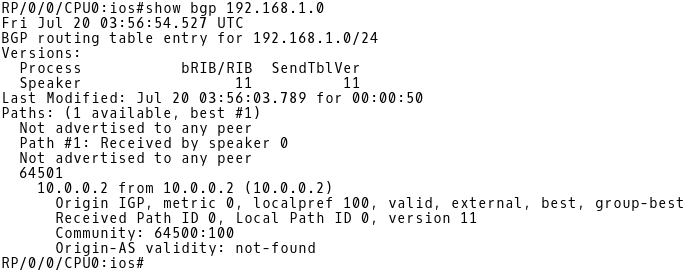
Picture 2: Inspecting BGP Table of IOS-XR for 192.168.1.0/24
2. BGP Attribute Filtering Configuration – Action Treat-As-Withdraw
Now let’s configure an action treat-as-withdraw on IOS-XR for the attribute community. First, create attribute-filter group WITHDRAW. Then assign the attribute community to the group with the action treat-as-withdraw.
RP/0/0/CPU0:ios(config)# router bgp 64500 RP/0/0/CPU0:ios(config-bgp)# attribute-filter group WITHDRAW RP/0/0/CPU0:ios(config-bgp-attrfg)# attribute COMMUNITY treat-as-withdraw RP/0/0/CPU0:ios(config-bgp-attrfg)# exit
As the next step, configure the inbound BGP Update message handling for the 10.0.0.2 neighbor. Then assign the attribute-filtering group WITHDRAW to the neighbor.
RP/0/0/CPU0:ios(config-bgp)# neighbor 10.0.0.2 RP/0/0/CPU0:ios(config-bgp-nbr)# update in filtering RP/0/0/CPU0:ios(config-nbr-upd-filter)# attribute-filter group WITHDRAW
As the last step, commit the configuration.
RP/0/0/CPU0:ios(config-nbr-upd-filter)# commit
Once you commit the configuration, a logging message will inform you about filtering the attribute 8 – community from UPDATE message received from the neighbor 10.0.0.2 (Picture 3).

Picture 3: Routing-BGP-5-UPDATE_FILTERED Message generated by IOS-XR
The action treat-as-withdraw is taken for the 192.168.1.0/24 prefix, which means that the prefix is filtered from the BGP table of IOS-XR. Only the 192.168.2.0/24 prefix is presented in the BGP table (Picture 4).
RP/0/0/CPU0:ios# show bgp | begin BGP scan
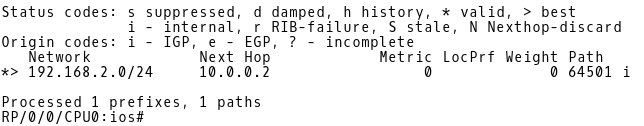
Picture 4: BGP Table of IOS-XR
Below is the entire BGP configuration of IOS-XR for reference.
RP/0/0/CPU0:ios# show running-config | begin bgp router bgp 64500 attribute-filter group WITHDRAW attribute COMMUNITY treat-as-withdraw bgp router-id 1.1.1.1 address-family ipv4 unicast neighbor 10.0.0.2 remote-as 64501 update in filtering attribute-filter group WITHDRAW update-source Loopback0 address-family ipv4 unicast route-policy PASS in route-policy PASS out
3. BGP Attribute Filtering Configuration – Action Discard
We only change an action inside the group WITHDRAW from withdraw to discard. The filtering configuration under the neighbor 10.0.0.2 section remains the same.
RP/0/0/CPU0:ios(config)# router bgp 64500 RP/0/0/CPU0:ios(config-bgp)# attribute-filter group WITHDRAW RP/0/0/CPU0:ios(config-bgp-attrfg)# attribute COMMUNITY discard RP/0/0/CPU0:ios(config-bgp-attrfg)# exit
As the last step, commit the configuration.
RP/0/0/CPU0:ios(config-nbr-upd-filter)# commit
Once you commit the configuration, a logging message will inform you about filtering the attribute 8 – community from UPDATE message received from the neighbor 10.0.0.2 (Picture 5).

Picture 5: Routing-BGP-5-UPDATE_FILTERED Message generated by IOS-XR
The action discard is taken for the prefix 192.168.1.0/24 which means that the attribute community is filtered from the prefix. However, the 192.168.1.0 prefix remains presented in the BGP table of IOS-XR. (Picture 6).
The difference between an action treat-as-withdraw and discard is obvious. While treat-as-withdraw action purges an entire prefix from the BGP table when a particular path attribute is matched inside the UPDATE message, the action discard only removes the attribute and the prefix is kept present in the BGP table.
RP/0/0/CPU0:ios# show bgp 192.168.1.0
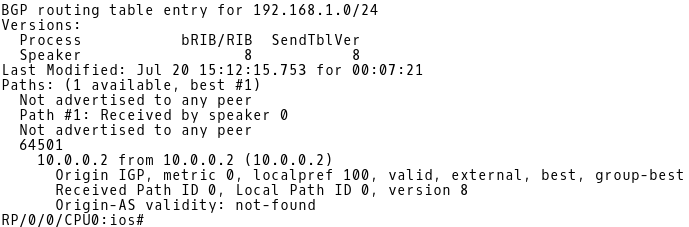
Picture 6: BGP Table of IOS-XR
Below is the entire BGP configuration of IOS-XR for reference.
router bgp 64500 attribute-filter group WITHDRAW attribute COMMUNITY discard bgp router-id 1.1.1.1 address-family ipv4 unicast neighbor 10.0.0.2 remote-as 64501 update in filtering attribute-filter group WITHDRAW update-source Loopback0 address-family ipv4 unicast route-policy PASS in route-policy PASS out
Conclusion:
BGP Attribute Filtering provides an increased measure of security. If the specified path attribute is matched in an UPDATE message, the attribute is either dropped and the UPDATE message is processed normally (action discard) or prefix is removed from the routing table (action treat-as-withdraw). The BGP Enhanced Attribute Error Handling feature prevents peer sessions from flapping due to errors from a malformed update. The established sessions are maintained and the valid routes are exchanged but the routes in a malformed UPDATE message are removed. It helps to minimize the malformed UPDATE message impact on routing and significantly saves the resources.