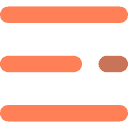
While networks are agnostic to the content of the serviced packets, end users have a very good understanding of what traffic they have and what is the expected shape of well behaved traffic. It is increasingly useful to pass and make use of such information upstream in order to better address the increasing risk of abusive or misbehaving traffic. This information needs to cross network boundaries while still being part of established trust domains. The presence of BGP sessions between networks indicates a good trust relationship between them and FlowSpec exploits this to facilitate passing traffic shape information either between routers, routing domains or networks.
While networks are agnostic to the content of the serviced packets, end users have a very good understanding of what traffic they have and what is the expected shape of well behaved traffic. It is increasingly useful to pass and make use of such information upstream in order to better address the increasing risk of abusive or misbehaving traffic. This information needs to cross network boundaries while still being part of established trust domains. The presence of BGP sessions between networks indicates a good trust relationship between them and FlowSpec exploits this to facilitate passing traffic shape information either between routers, routing domains or networks.
Examples of expected well behaved traffic from an end user’s perspective might be:
- an online shop’s 90+% of customers originate in Europe and US with very few visits from elsewhere. Rate limiting traffic from elsewhere at for example 1000Mbps will cover the needs of those few visitors during normal use and will protect the network in case of abusive spikes from most probably malicious attacks.
- a bank’s policy is to prohibit Bittorrent use. This could be enforced by dropping all packets targeting Bittorrent port ranges.
- a video conferencing service uses UDP to pass most of the live and time-sensitive content. This is achieved best by redirecting UDP ‘flows’ directly to the forwarding farms while routing the typical session setup or authentication TCP flows to ordinary web farms.
Even when this information cannot propagate upstream, being able to enforce policies at the network’s edge brings many benefits including advance planning and preparation. This allows networks to start using the technology even when their neighbors and upstream providers are not yet ready to support it. Of course, the full potential of BGP FlowSpec is reached when this traffic shape information propagates and is enforced as far upstream as possible. This might take time and this depends on wide BGP FlowSpec adoption by networks.
The main factors for BGP FlowSpec broader adoption are:
A. complexity that network administrators need to balance against benefits the technology brings.
B. technological design flaws that limit the use cases that address varying network needs.
C. scalability and computational constraints imposed by the technology on networking equipment.
D. acceptance by neighbors increases the utility of the technology. Of course, acceptance usually increases as the technology matures.
For example adopters of BGP FlowSpec report the following issues during early adoption:
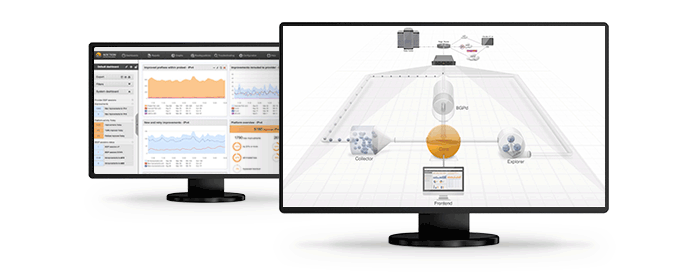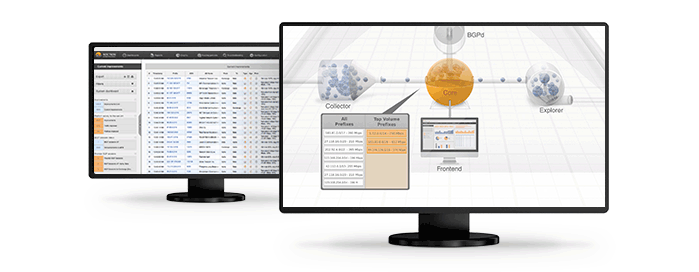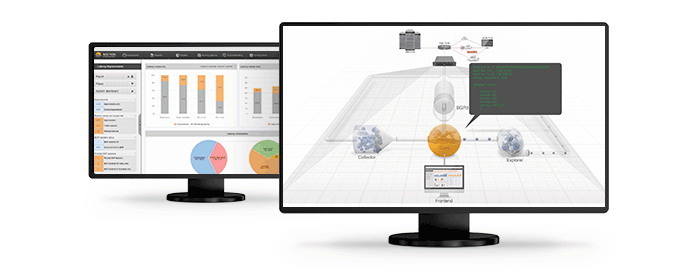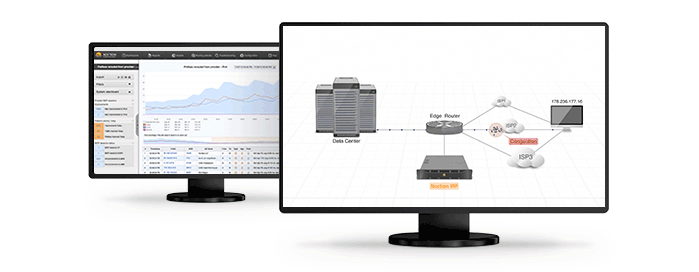
- scaling issues where BGP FlowSpec capable routers hit their CPU limits while trying to enforce FlowSpec traffic shaping rules. These days some of our customer testimonials show us that their network has been tested to perform admirably even with tens of thousands of FlowSpec rules.
- implementation bugs were another significant reason. Many years have passed and most of the bugs have been addressed.
- design limitations made BGP FlowSpec less useful for many networks. In the meantime the initial RFC5575 has been supplemented with additional capabilities to address many other network use cases.
 Networks are likely to implement BGP FlowSpec in the near future. At least these are the findings of a survey carried out by Juniper. The scale to the right highlights how likely individual networks assess whether they will implement BGP FlowSpec. Less than 5% of the respondents are very unlikely to implement it while more than one third are very likely to introduce the technology even in their current environment. Even those who currently do not intend to introduce BGP FlowSpec, most do not hold a very strong opinion against it and clearly indicate a willingness to reconsider once the environment becomes more favorable (perhaps more widely adopted).
Networks are likely to implement BGP FlowSpec in the near future. At least these are the findings of a survey carried out by Juniper. The scale to the right highlights how likely individual networks assess whether they will implement BGP FlowSpec. Less than 5% of the respondents are very unlikely to implement it while more than one third are very likely to introduce the technology even in their current environment. Even those who currently do not intend to introduce BGP FlowSpec, most do not hold a very strong opinion against it and clearly indicate a willingness to reconsider once the environment becomes more favorable (perhaps more widely adopted).
Networks are ready to implement BGP FlowSpec as they can do it gradually, while becoming more comfortable with its capabilities. Along the way, more confidence and experience is gained with its deployment.
Noction strives to include BGP FlowSpec capabilities into IRP in such a manner that keep complexity under control and specifically allow easy definition and review of BGP FlowSpec policies. Once the complexity issue is addressed Noction believes its customers will gradually increase their reliance on this technology in order to reap the ever increasing benefits.
Of course, there have been notable horror stories with BGP FlowSpec implementations. A few words regarding the well publicized CloudFlare outage of 2013 that put BGP FlowSpec in the spotlight as for example reported in a postmortem here
Indeed, it was a catastrophic event that affected a well known Internet player. Still it was just another case of an implementation bug that as reported by CloudFlare itself: “What happened instead is that the routers encountered the rule and then proceeded to consume all their RAM until they crashed.” The incident helped BGP FlowSpec implementations become more resilient and better designed, just like any other maturing technology. Three years have passed without similar cases and it is the time that we more broadly started using this technology.